Do you know what is happening in the background when you buy something in an online shop using PayPal?
In this post we will tackle the following problems:
- How can PayPal's API be tested?
- How does PayPal's Express Checkout work? You can find the detailed report here.
- How can we debit more money than authorized?
How PayPal's API can be tested?
PayPal's Sandbox API
PayPal offers a feature called PayPal Sandbox Accounts, which mimics the production API. The basic idea is that a normal user/shop can test the API and make transactions without actually transferring money. This is the perfect tool for developers to test their API integration.Access to all messages
The next question is how to get access to all messages. All browser-related messages can be inspected, intercepted, and modified via BurpSuite. The main problem here is how to get access to the server-to-server exchanged messages: the messages exchanged between PayPal and a shop. In order to solve this problem, we deployed our own shop. For this purpose we used Magento, which already has a PayPal integration.Once we have our own controlled shop, we can enforce Magento to send all request through a proxy.
In the following picture you can see our setup.
 |
| Test suite for analyzing PayPal's API [1] |
In order to capture the traffic between our Magento hhop and PayPal we proceeded as follows:
- We configured Magento to use a proxy running on localhost:8081.
- We connected the proxy port on the virtual machine with our local machine via SSH remote port forwarding by issuing the following command
- We configured BurpSuite running on our local machine to listen on Port 8081 for incoming requests.
Please note that we uses our own, custom Magento shop in order to be able to test Paypal's API.
PayPal's Express Checkout
An overview of the checkout procedure is depicted in the following: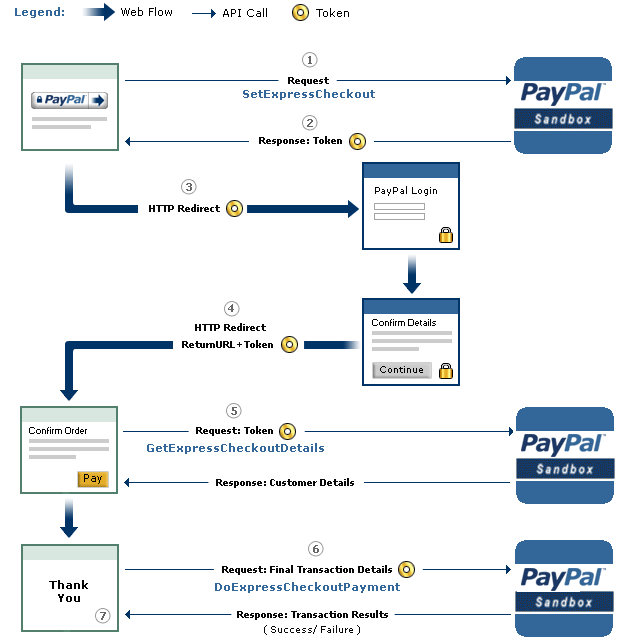 | ||||
| PayPal's Express Checkout [2] |
Step 1: Magento tells the PayPal API where to redirect the user after authorizing the transaction via the parameter RETURNURL and requests a token for this transaction.
Step 2: The PayPal API provides Magento with the token.
Step 3: Magento redirects the user to PayPal's website. The redirect contains the token from the previous step.
Step 4: The user authorizes the transaction. As a result, he will be redirected back to Magento (RETURNURL) with the token.
Step 5: Magento issues a request to the PayPal API to get the transaction details.
Step 6: Magento signals the PayPal API to execute the transaction.
Step 7: Magento serves the success page.
A more detailed view of the protocol and all parameters is shown on page 16 in the full version. We will concentrate only on step 6 and the parameters relevant for the attack.
The Attack
The goal of the attack is to let a shop (in our case Magento) debit more money than authorized by the PayPal user. The core of the attack is Step 6 -- DoExpressCheckoutPayment. Let's get a deeper look at this message: |
| Magento can raise the authorized amount and debit more money from the user's account |
- The shop sends the token, which was issued in the first step of the protocol and identifies uniquely the transaction through all steps.
- The PayerID referring to the user that authorized the payment.
- The AMT defining the amount, which will be transferred.
- The API Credentials authenticating Magento on PayPal.
- The Version pointing to the release number of the API.
As one can imagine, the core problem we found was the change of the AMT parameter. This value can be freely chosen by the shop, despite the fact that the user has authorized a different amount.
We tested only the SandBox API, but refused to test the production API in order to avoid problems. We promptly contacted PayPal's security team and described the problem hoping that PayPal can and will test the production API against the attack.
The response of PayPal can be summarized as follows:
- We don't get any BugBounty since we only tested the Sanbox API. (Fair enough)
- In the Production API PayPal this flexibility is a wanted feature. Thus, PayPal allows a merchant to charge for shipping and/or other expenses different amounts. Any malicious behavior can be detected by PayPal. In case of fraudulent charges the consumer are protected by the Buyer Protection policy.
Authors of this Post
Daniel HirschbergerVladislav Mladenov
Christian Mainka (@CheariX)
[1] BurpSuite Logo
[2] PayPal Express Checkout




